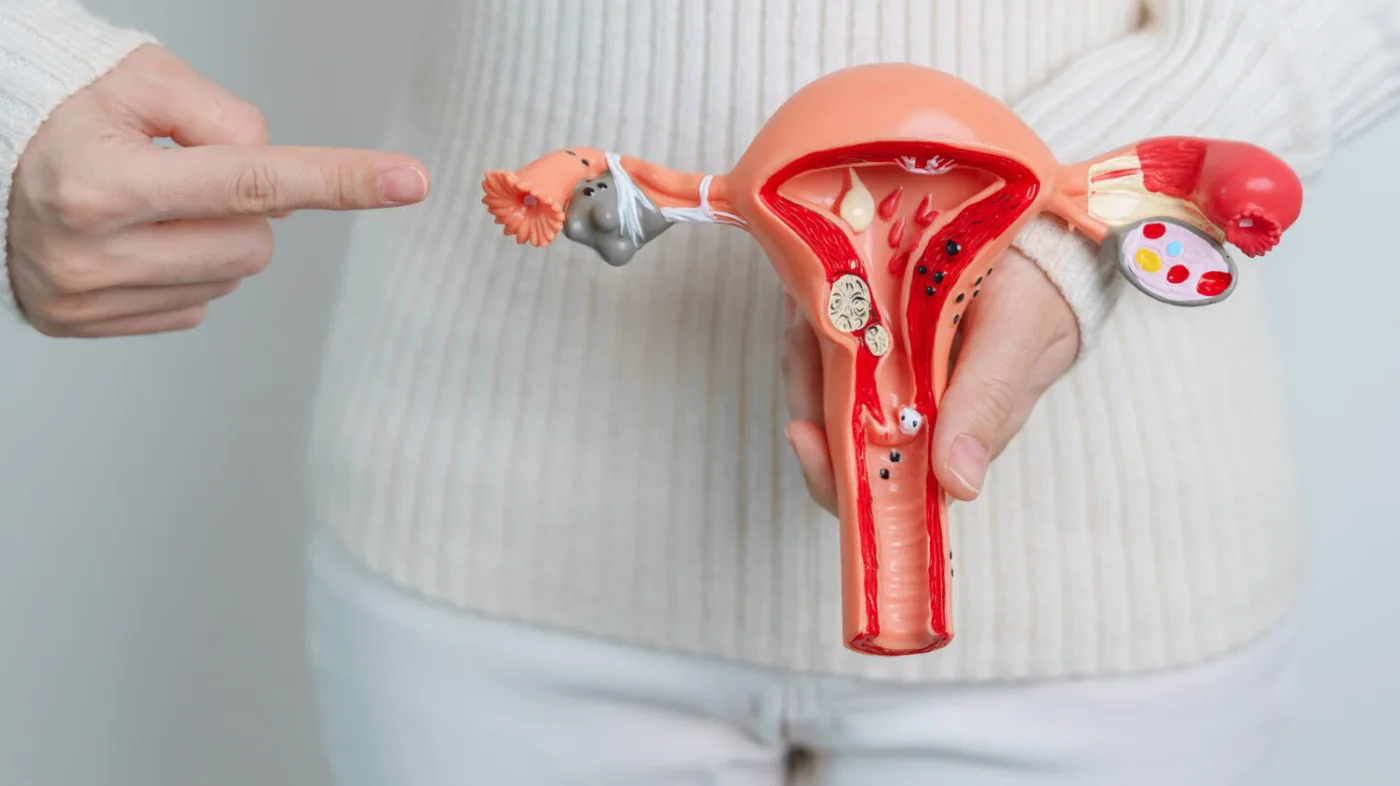
Some women might feel worried if they experience symptoms of granulation tissue after hysterectomy. This article will help you understand the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for granulation tissue post-hysterectomy.
What Is Granulation Tissue?
Granulation tissue formation is a common part of the healing process in wounds and surgical sites. But how can it become a cause for concern? And what are the telltale signs you should be aware of?
Characteristics of Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. It’s usually pink or red and has a granular appearance. Typically, it’s a good sign that your body is healing correctly. However, excessive granulation tissue, or “hyper-granulation,” can hinder the healing process.
Granulation Tissue vs. Normal Healing Process
While formation of granulation tissue is a part of a normal healing process, too much of it, or hyper-granulation, can create complications. In many cases, these complications can cause discomfort and require additional medical intervention.
Symptoms of Granulation Tissue After Hysterectomy
After a hysterectomy, it’s critical to identify the symptoms of granulation tissue. Noting these symptoms promptly can help ensure proper and timely medical intervention.
Post-Hysterectomy Bleeding
One of the primary symptoms of granulation tissue post-hysterectomy is unexpected and prolonged bleeding. Often, this isn’t just spotting, but heavy, persistent bleeding. If you notice this, it’s crucial to reach out to your healthcare provider immediately.
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain, particularly when localized in the area of surgery, could be another symptom. Pain may vary in intensity and often increases during sexual intercourse or physical activities.
Vaginal Discharge
Vaginal discharge, particularly foul-smelling, could signify infection or granulation tissue development. It’s essential to pay attention to these changes in your body.
The Other Less Common Symptoms
Feeling a mass or tenacious tissue in the vaginal canal or experiencing recurrent lower urinary tract infections are also symptoms, although less common.
Why is Granulation Tissue a Concern After a Hysterectomy?
While granulation tissue is a part of the healing process, after a hysterectomy, its formation can cause certain complications.
Delayed Healing
Excessive granulation tissue can obstruct the normal repair process of surgical wounds, leading to increased healing times.
Quality of Life Impact
The symptoms associated with granulation tissue, such as pelvic discomfort and abnormal bleeding, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
What Treatments Are Available?
If you suspect the presence of granulation tissue post-hysterectomy, remember, you’re not alone. Reach out to your healthcare provider. The good news is, several treatment options are available.
Silver Nitrate
For many healthcare providers, the first line of treatment is applying silver nitrate, a substance that helps remove granulation tissue.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids creams can help reduce inflammation and retard the formation of granulation tissue.
Surgical Removal
In rare cases where conservative methods prove ineffective, surgical removal of the granulation tissue might be necessary.
Here are your amended paragraphs, including appropriate local placement of your selected keyword:
1. Understanding the Symptoms of Granulation Tissue after Hysterectomy
Understanding your healing journey after a hysterectomy is crucial to maintain optimal health. One important factor to keep in mind is granulation tissue that develops post-surgery. The symptoms of granulation tissue after hysterectomy can be diverse and somewhat concerning if you’re not familiar with them. Make sure to spot signs such as unusual discharge, unusually prolonged or intensified pain, and bleeding that’s not linked to menstruation.
2. Deciphering the Symptoms of Granulation Tissue after Hysterectomy
Deciphering the symptoms of granulation tissue might seem complex, but it doesn’t have to be. Continual care and vigilance are essential during recovery. Post-procedure signals like persistent discomfort, abnormal bleeding, and unfamiliar discharge patterns could potentially indicate the presence of granulation tissue, a common occurrence after hysterectomy.
3. The Common Symptoms of Granulation Tissue after Hysterectomy
It’s normal to have questions about what to expect during your healing stage after a hysterectomy. Granulation tissue, which commonly occurs post-surgery, can manifest some particular symptoms. The most common treatment for granulation tissue after hysterectomy include ongoing pain different from expected post-surgery discomfort, discharge that isn’t typical, and unanticipated prolonged bleeding.
4. Symptoms to Track: Granulation Tissue after Hysterectomy
When keeping a watchful eye on your post-hysterectomy progress, be mindful of the symptoms of granulation tissue. This tissue frequently develops after surgery, and its symptoms might require attention. Signs such as chronic non-menstrual bleeding, unusual discharge, and pain that seems incongruous with standard postoperative discomfort could highlight the formation of granulation tissue after hysterectomy.
5. Identifying the Symptoms of Granulation Tissue after Hysterectomy
Identifying the symptoms of granulation tissue after a hysterectomy is paramount on your road to recovery. Granulation tissue, a common occurrence after this surgery, can give signals that might warrant consultation with your healthcare provider. Be vigilant for persistent pain that goes beyond normal post-surgery discomfort, unusual discharge, and prolonged bleeding to ensure a healthy recovery.
Understanding the Symptoms of Granulation Tissue after Hysterectomy: Postoperative Bleeding
Postoperative bleeding within 10-14 days after a hysterectomy may occur due to the evacuation of a hematoma situated at the top of the vagina. Alternatively, bleeding may also be conspicuous once sexual activities are resumed, indicating a manifestation of the treatment for granulation tissue after hysterectomy. This symptom, often connected to the late onset bleeding due to the vascular healing tissue, also known as granulation tissue inside the vault, isn’t uncommon. The patient may notice sensitivity accompanied by some bleeding. A method commonly employed to cauterize this tissue involves using silver nitrate. However, if the granulation tissue is notably copious, it might necessitate removal in a surgical theater.
Preparing for a Hysterectomy: Preoperative Measures to Curb Symptoms of Granulation Tissue
In the week leading up to the surgery, to optimize your recovery after the removal of the uterus, it’s essential to prevent constipation as pain relief drugs can exacerbate it. A combination of coloxyl, agarol, metamucil, and abundant hydration can significantly mitigate the likelihood of experiencing symptoms of granulation tissue after hysterectomy.
The Aftercare: Steering the Recovery Process Post-Hysterectomy
The nature and level of care you will need postoperatively will vary according to the specific procedure carried out. For abdominal incisions, dressings that are removed within 24-48 hours will cover the wounds. Sometimes, dressings might appear bloodstained due to sutures passing through minor vessels in the skin and subsequent oozing.
In cases of a vaginal hysterectomy, a pack may be inserted into the vagina to limit blood loss, one consequence which may relate to the symptoms of granulation tissue after hysterectomy. While this pack typically is removed the next morning, it can potentially cause some discomfort overnight. It’s also crucial to monitor any vaginal loss post-hysterectomy.
To minimize the risk of deep vein thrombosis and further aid your recovery, mobilization may be recommended the following day based on your comfort level. Every patient will have a catheter in the bladder, usually removed on the subsequent morning.
Read more: Neutrogena hydro boost gel cream ingredients