A 32-year-old man was taken into medical care due to a progressive decline in breath control coupled with a non-productive cough that had persisted for three months. In the course of his clinical examination, significant symptoms were recognized. These included a high pulse rate of 118 beats per minute, hypotension with a blood pressure reading of 100/60 mm Hg exhibiting pulsus paradoxus, visibly distended jugular veins and subdued heart sounds.
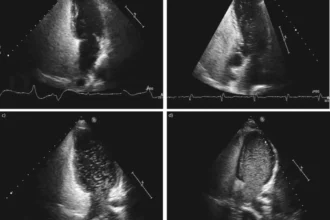
Notable characteristics on the electrocardiogram (ECG) suggested a dire pericardial effusion accompanied by cardiac tamponade, consisting of sinus tachycardia, diminished QRS voltages and electrical alternans (QRS complex showing variable amplitude and axis from beat to beat) (Figure 1A). Further credence to the diagnosis was provided by transthoracic echocardiography.
An executed pericardiocentesis procedure helped drain approximately 1 liter of bloody fluid, which, upon scrutiny, indicated malignancy, indicative of adenocarcinoma. Computed tomography scans of chest and abdomen revealed a pericardial effusion, pleural effusion on both sides and numerous hypodense liver lesions (Figure 1B).
However, before the complete diagnostic evaluation, the patient sadly suffered a cardiac arrest and passed away.
Diagnosis of Cardiac Tamponade: A Visual Journey through ECG and CT Scan Findings
Figure 1 encapsulates the significant diagnostic findings: (A) ECG depicting the characteristic trio of symptoms for cardiac tamponade – sinus tachycardia, weak QRS voltages and electrical alternans (pointed out using arrows). (B) CT scan exposes pericardial effusion with the pericardiocentesis catheter neatly in place (marked using an arrow), and bilateral pleural effusion. Click to open in a new tab, or download for more detailed examination.
Electrical alternans, characterized by fluctuating QRS voltage, signifies a grave indication of extensive pericardial effusion with tamponade on ECG, despite being a less sensitive finding. This condition manifests due to the periodic front-back heart swing within the ample effusion and is often a feature of malignant etiologies like metastatic lung or breast cancer. This feature may also elevate the risk of ventricular arrhythmias and is most conspicuous in the mid-chest leads. The ECG hallmark trio – sinus tachycardia, reduced QRS voltage, and electrical alternans – provides a near definitive diagnosis for cardiac tamponade, albeit observed in a reduced patient subset.
Cardiac Tamponade ECG Findings: An Insightful Guide
In the universe of cardiovascular health, “cardiac tamponade” might sound like a distant world. Here’s your roadmap to understanding the ECG findings linked to this intriguing-yet-frightening condition.
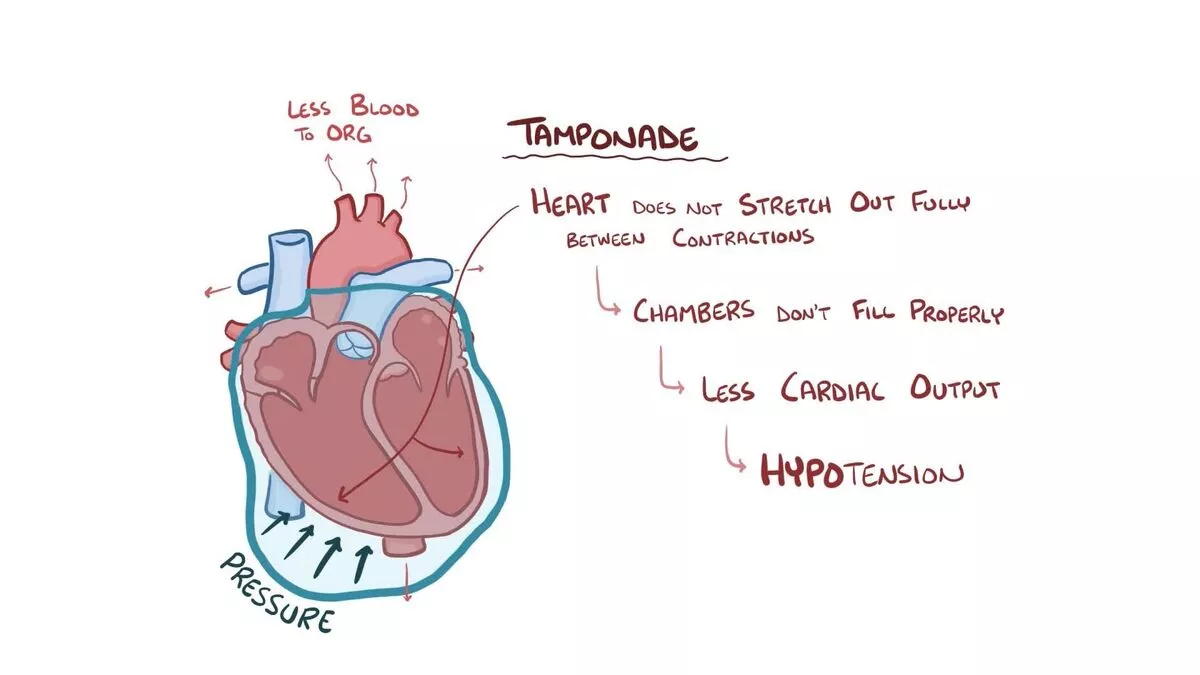
Imagine being in space without a spacesuit, with pressure building up – a problematic situation, right? That’s what your heart might feel like when the pericardial space is filled with excess fluid or blood due to medical conditions such as infections, injury, or heart surgery – a condition known as Cardiac Tamponade.
Interpreting the Basics:
What Is Cardiac Tamponade?
Ever found yourself trying to squeeze an overfilled water balloon? That’s what the heart faces in Cardiac Tamponade. With intensified pressure, the heart struggles to function, leading to critical symptoms like chest pain and breathlessness.
Wave Of Signals: The ECG
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) can be seen as a meteorologist for the heart, predicting its functional forecast. It records the heart’s electrical activity, indicating any potential storm brewing.
ECG Findings in Cardiac Tamponade
Before we take a deep dive into the ocean of ECG findings, remember the basic ECG wave pattern? The P waves, QRS complex, and T waves – each of which corresponds to particular heart activities.
Reduced Voltage
It’s like a dimmed lighthouse on a stormy night. The QRS complex on an ECG shows unexpectedly low voltage, which is often the first ECG sign of cardiac tamponade.
Electrical Alternans
A distinctive yet fascinating ECG phenomenon is ‘Electrical Alternans,’ a sign of cardiac tamponade. Much like a swing of a pendulum, there’s an apparent alternation in the amplitude or axis of the QRS complex on an ECG, which signifies severe fluid accumulation.
Tachycardia
Imagine your heart on a treadmill, unwillingly. Rapid heart rate or ‘tachycardia’ is a common symptom and ECG finding in cardiac tamponade, something akin to a rabbit running in overdrive.
Sinus Tachycardia
Often with cardiac tamponade, the ECG might show ‘Sinus Tachycardia,’ a specific type of rapid heartbeat originating from the Sinus node, just like a drummer performing a solo at a high tempo.
Non-specific ST-T Changes
Jumbled puzzle pieces – that’s what Non-specific ST-T changes often are. These can occur due to myocardial ischemia induced by the raised intrapericardial pressure.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
A Saving Straw: Echocardiogram
For a cardiac tamponade diagnosis, an Echocardiogram acts as a crucial lifesaver. It’s like using a telescope to view the deep sky – offering direct vision of the fluid around the heart.
Easing Off The Pressure: Pericardiocentesis
Picture this as a pressure release valve. Pericardiocentesis, the procedure to remove fluid from the pericardial space, is often the required emergency treatment.
FAQs about Cardiac tamponade ecg findings
- What exactly is ‘cardiac tamponade’? Cardiac tamponade is a severe medical condition wherein fluid accumulates in the pericardial space around the heart, limiting its ability to pump blood effectively.
- What are the primary ECG findings in cardiac tamponade? Key ECG findings include low voltage QRS complexes, Electrical Alternans, Tachycardia, Sinus Tachycardia, and non-specific ST-T changes.
- What’s ‘Electrical Alternans’? Electrical Alternans is an ECG phenomenon that involves alternating amplitude or axis of the QRS complexes. It is a sign of severe fluid accumulation around the heart.
- Can cardiac tamponade be treated? Yes, cardiac tamponade requires urgent treatment which often involves an emergency procedure called ‘pericardiocentesis’ to remove the accumulated fluid from around the heart.
- How is cardiac tamponade diagnosed? While ECG provides critical signs, Echocardiography is the most widely used diagnostic tool for cardiac tamponade.
In Conclusion about Cardiac tamponade ecg findings
You’ve now embarked on a journey through the universe of cardiac tamponade, touching down at the intriguing planet of ECG findings.
The importance of understanding ECG findings in cardiac tamponade cannot be overstated. The unique ECG characteristics can act as a lighthouse in a storm, guiding clinicians towards a potentially life-saving diagnosis.
Read more: Groin hematoma after cardiac catheterization